The Cisco ® Coarse Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (CWDM) Gigabit Interface Converter (GBIC)/Small Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) solution allows enterprise companies and service providers to provide scalable and easy-to-deploy Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel services in their networks. The product set helps enable the flexible design of highly available, multiservice networks.
The Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP solution is a convenient and cost-effective solution for the adoption of Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel in campus, data-center, and metropolitan-area access networks.
The Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP solution has two main components (Figure 1): a set of eight different pluggable transceivers (Cisco CWDM GBICs and Cisco CWDM SFPs), and a set of different Cisco CWDM passive multiplexer/demultiplexer or optical add/drop multiplexers (OADMs). A Cisco CWDM chassis enables rack-mounting up to two of the Cisco CWDM passives. Both the transceivers and the passive multiplexers are compliant with the ITU-T G.694.2 standard defined CWDM grid.
Figure 1. Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP Solution
KEY FEATURES AND BENEFITS
Scalability
The Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP solution helps enable the transport of up to eight channels (Gigabit Ethernet or Fibre Channel) over single-mode fiber strands.
Easy Deployment and Flexible Implementation
The Cisco CWDM GBIC (and Cisco CWDM SFP) fits into a standard GBIC (and SFP) port supporting the IEEE 802.3z standard on the supported Cisco Systems ® platforms. The Cisco CWDM OADM is passive and requires no power. Neither the Cisco CWDM GBIC (nor Cisco CWDM SFP) nor the Cisco CWDM passives requires configuration.
The Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP solution allows for a variety of network configurations-from multichannel point-to-point to hub and meshed-ring configurations.
High Availability
The Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP solution takes advantage of a multichannel architecture and the inherent protection of ring architectures. The solution helps enable:
• Use of Layer 2 and Layer 3 redundancy and failover mechanisms at the channel endpoints (Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP) to build highly available links
• Use of two-path link configurations in a ring architecture to provide protection from fiber cuts
Investment Protection
The Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP solution helps enable enterprises and service providers to increase the bandwidth of an existing Gigabit Ethernet optical infrastructure without adding new fiber strands. The solution can be used in parallel with other Cisco GBIC and SFP devices on the same platform.
DEPLOYMENT SCENARIOS
Point-to-Point Configuration
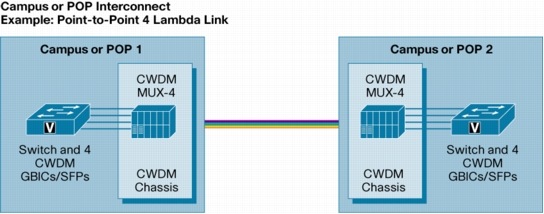
In a point-to-point configuration (Figure 2), two endpoints are directly connected through a fiber link. The Cisco CWDM GBIC/SFP solution helps enable customers to add or drop as many as eight channels (Gigabit Ethernet or Fibre Channel) into a pair of single-mode fiber strands. As a result, the need for additional fiber is minimized. Redundant point-to-point links are possible by adding or dropping redundant channels into a second pair of single-mode fiber strands.
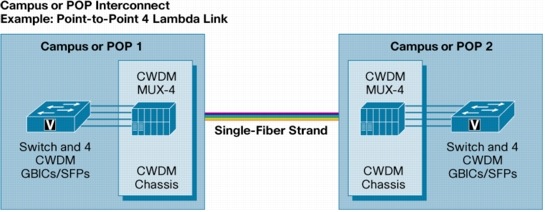
A single fiber point-to-point configuration also is possible (Figure 3). By using different wavelengths to transmit and receive signals, as many as four channels can be transported over a single fiber strand.
The main applications for the architecture are enterprise campus links and service provider point-of-presence (POP) or hub interconnects across a metropolitan (metro) area.
Figure 2. Point-to-Point Architecture (Dual-Fiber Link)
Figure 3. Point-to-Point Architecture (Single-Fiber Link)
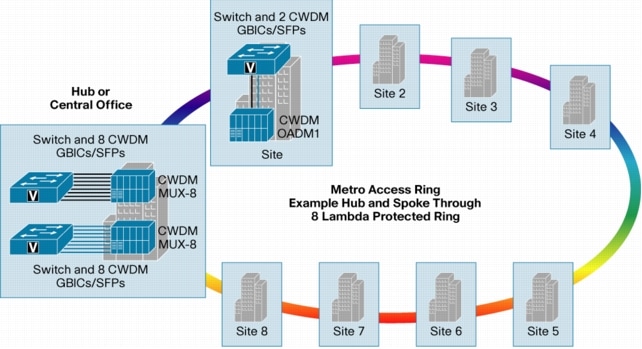
Hub-and-Spoke (Ring) Configuration
In a hub-and-spoke configuration (Figure 4), multiple nodes (spokes) are connected with a hub location through a ring of single-mode fiber. Each hub-node connection can consist of a single or multiple channels. Protection from fiber cuts in the ring is achieved by connecting the hub and nodes through both directions of the optical ring. Service provider metro access rings are the main applications for this architecture.
Figure 4. Hub-and-Spoke (Ring) Architecture
Mesh (Ring) Configuration
Mesh deployments are a combination of hub-and-spoke and point-to-point or even multiple point-to-point connections in parallel on the same optical link. Deployment of the maximum eight wavelengths allows for different combinations of these scenarios.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Cisco CWDM GBICs
The Cisco CWDM GBIC (Figure 5) is a hot-swappable input/output device that plugs into an 802.3z standards-compliant GBIC port or slot of a Cisco switch or router, linking the port with the fiber-optic network.
Figure 5. Cisco CWDM GBICs
Performance
• 1.25 Gbps full-duplex links
• Optical link budget of 30 decibels (dB)
Platform Support
The Cisco CWDM GBICs are supported across a variety of Cisco switches, routers, and optical transport devices. For more details, refer to the document Cisco CWDM GBIC Compatibility Matrix.
Connectors and Cabling
• Equipment: Standard GBIC interface
• Network: Dual SC/PC connector
Note: Only connections with patch cords with PC or UPC connectors are supported. Patch cords with APC connectors are not supported.
Environmental Conditions and Power Requirements
The operating temperature range is between 32 and 122°F (0 and 50°C); storage temperature range is between -40 and 185°F (-40 and 85°C). Table 1 provides the electrical power interface details, and Table 2 describes optical parameters.